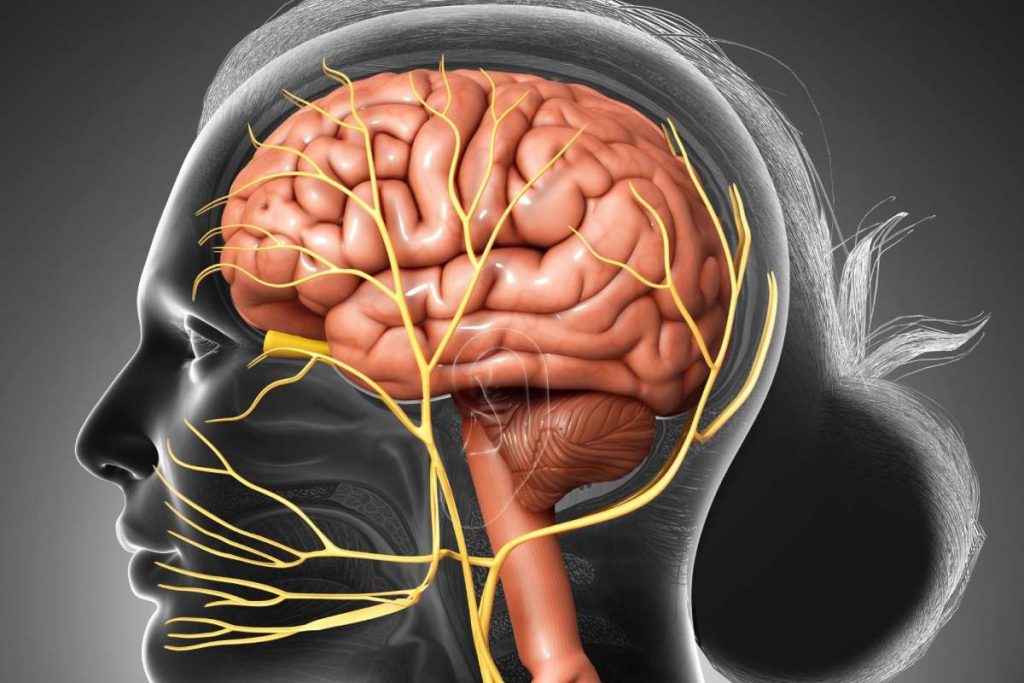
Infundibulum Brain – A conical outpouching from an artery, typically intracranial, known as an infundibulum (plural: infundibula), has a broad base and a tiny apex from which a vessel emerges. The cause of the posterior communicating artery (PCOM) from the supraclinoid internal carotid artery is where an infundibulum is most frequent find. They can see in up to 25% of cerebral angiograms.
An infundibulum’s principal significance is that it could misinterpret for a saccular (berry) aneurysm (which is round and has a branch at its base). Most of the time, an infundibulum is smaller than 3 mm. Unlike an aneurysm, an infundibulum (infundibulum brain) not supposes to pose a threat of rupture and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Therefore, an infundibulum brain rarely becomes an aneurysm 1. It is typically not believed that an incidental infundibulum brain must follow up on unless there are other signs of clinical concern. Large size, a family history of subarachnoid hemorrhage or aneurysm, connective tissue problems, a history of dissection, or aneurysm elsewhere are prudent indicators that follow-up may be necessary.
Table of Contents
What Is The Brain?
The brain is a complex organ that manages every bodily function as well as thought, memory, emotion, touch, temperature, motor skills, respiration, vision, and starvation. The spinal cord that protrudes from the brain is part of the central nervous system or CNS.
What Is The Part Of The Brain?
The cerebellum, also called the “little brain,” is a fist-sized section situated in the head’s rear, above the brainstem and the temporal and occipital lobes. It features two hemispheres, just like the cerebral cortex. The inner region connects with the cerebral cortex, while the outer part contains neurons.
What Is The Brain Made Of?
The brain is around 60% fat and weighs about 3 pounds in a typical adult. Combinations of water, protein, carbs, and salts make up the remaining 40%. The brain is not a muscle in and of itself. Instead, it comprises nerves, blood vessels, neurons, and glial cells.
How Does The Brain Work?
The brain connects with the rest of the body via electrical and chemical impulses. Your brain interprets each signal, which controls a distinct process. For instance, some make you feel worn out, while others make you uncomfortable.
Some messages storing in the brain, though others transmit to distant extremities through the spine and the extensive network of nerves in the body. The central nervous system uses billions of neurons to accomplish this (nerve cells).
Where Is Infundibulum Brain Located?
right ventricle
The region of the right ventricle that resembles a funnel and opens into the pulmonary artery is called the Infundibulum (Latin for “funnel”). Infundibular stenosis is another name for the narrowing of it.
What Does The Infundibulum Do In The Brain?
The infundibular stalk, also known as the Infundibulum(infundibulum brain) or pituitary stalk, is a tube-like structure that joins the hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary. It enables the posterior pituitary to send hormones made in the hypothalamus to circulation for release.
Is The Infundibulum Part Of The Brain?
Brain: The pituitary stalk, sometimes referred to as the Infundibulum or Infundibular Stalk, connects the posterior pituitary to the hypothalamus. The Infundibulum, or cup or funnel, is where a hair follicle develops.
What Is The Purpose Of The Infundibulum Brain?
The Infundibulum (infundibulum brain) catches and channels the released eggs; it is the wide distal (outermost) portion of each fallopian tube. The endings of the fimbriae extend over the ovary; they contract close to the ovary’s surface during ovulation to guide the free egg.
What Hormones Does The Infundibulum Brain Secrete?
These include beta-endorphin, prolactin, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), growth hormone (GH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH).
Does Pituitary Stalk Enhance?
The pituitary stalk always enhances following the introduction of contrast material. However, depending on the extent of the infundibular recess, an then uniformly enhancing stalk occasionally had a core patch of nonenhancement.
What Does The Infundibulum Brain Connect The Pituitary Gland To?
The infundibular stalk, also known as the Infundibulum (infundibulum brain) or pituitary stalk, is a tube-like structure that joins the hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary. It enables the posterior pituitary to send hormones made in the hypothalamus to circulation for release.
Is The Infundibulum Brain Part Of The Posterior Pituitary?
This area, which makes up most of the posterior pituitary and is also known as the neural lobe or posterior lobe, is where oxytocin and vasopressin are stored. Finally, the infundibular stalk, called the pituitary stalk or the Infundibulum, connects the hypothalamus and hypophyseal systems.
What Is The Gray Matter And White Matter?
Two distinct parts of the central nervous system are grey matter and white matter. Grey matter in the brain refers to the thicker outer layer, and white matter to the thinner inner layer beneath. This arrangement reverses in the spinal cord, where the grey matter locates within, and the white matter is on the outside.
Axons, the lengthy stems connecting neurons and covered with myelin, make up the majority of white matter. In contrast, neuron somas, the round core cell bodies, make up the majority of grey matter (a protective coating). The two appear as separate shades on some scans because of the differences in the composition of the neuron components.
Brain Tests
- CT scan: A scanner takes several X-rays, then processed by a computer to provide in-depth pictures of the brain and skull.
- An MRI scanner usages radio waves and a magnetic field to produce extremely fine-grained images of the brain and other regions of the skull.
- A particular material known as “a contrast agent” inject into the veins during an angiography (brain angiogram) and travels to the brain. Next, the brain is photographing using an X-ray machine, which can reveal issues with its arteries.
- A specific MRI scan of the arteries in the brain is called a magnetic resonance angiography (MRA). An MRA scan might detect a blood clot or another stroke-causing factor.
- A needle placing into the area around the spinal nerves during a lumbar puncture (called a spinal tap), and fluid draws out for examination. When meningitis is suspected, lumbar puncture is frequently performed.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): Electrodes apply to the skin of the head to record brain activity. EEG can use to diagnose seizures and other neurological conditions.
- Tests of short-term memory, problem-solving skills, and other sophisticated brain functions include in neurocognitive testing. In addition, neurocognitive assessment is frequent carry out using questionnaires.
- Rarely does a tiny piece of the brain require for a brain biopsy to diagnose a brain disorder. Therefore, brain biopsies are often only perform when the information is necessary to deliver appropriate care.
Conclusion
In all the above articles, we at vigorblog have discussed some important points related to Infundibulum Brain. We hope that the content information will be helpful.